
- RBI has lowered its reverse repo rate from 7.9% in 2015 to 3.35% in 2020/21.
- India’s industrial expansion slowed 4.6% in February 2021.
- The US is planning to impose close to $100 million in retaliatory tariffs on India.
The USD/INR trading pair closed on a high of 73.8270 on April 6, 2021, after opening the trading day on a low of 73.2019. The dollar inched up 0.83% against the Indian rupee ahead of the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) rate decision. The RBI lowered the reverse repo rate (which is the interest rate applied when the RBI borrows from commercial banks) to 3.35% from a high of 5.6% in FY 2019.
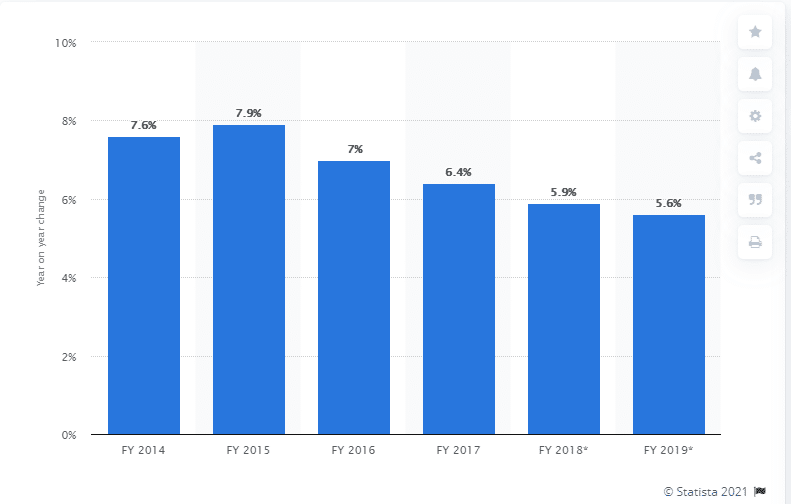
India’s Reverse rate since FY 2014
A lower reverse rate would mean that there is an increased money supply as commercial banks shift from depositing money with the RBI to individuals. Indian shares edged higher on April 7, 2021, with the decision to lower the rate seen as vital for the shift. There has been an increase in COVID-19 cases, with new cases close to the 100,000 mark as of April 5, 2021.
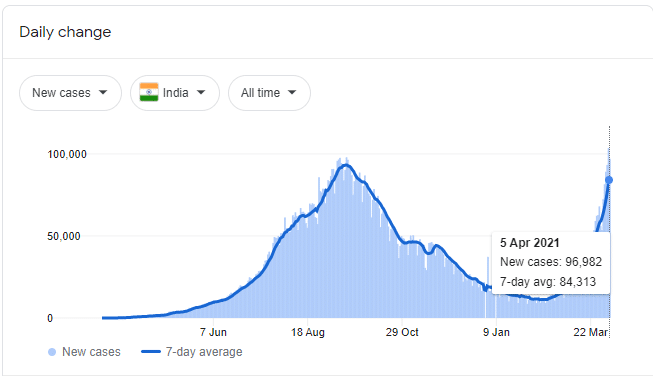
India’s Covid19 cases
The country has witnessed up to 166,000 deaths from 12.7 million cases since 2020.
Economy preparedness
India has embarked on a fast rollout of vaccines to successfully manage the second COOVID-19 wave. The country has managed to reduce deaths from a 7-day average of 1,167 at the end of Q3 2020 to 490 as of Q1 2021. February 2021 saw retail inflation rise to 5.03% (an increase of 0.97%) from 4.06% in January 2021. The increase was attributed to high food and fuel prices.
Grain production in the FY 2020-2021 rose to 303.3 million tonnes (a record increase for the 5th year running). Despite the decline in manufacturing PMI to 55.4 in March 2021, it still indicated slight expansion and growth. The effect was felt after eight industries contracted 4.6% in February 2021 from the industrial output of 1.6% a month earlier.
Trade relations
The Indian mass market is central to the US economic recovery, with a consumer market of more than 1 billion people. As of 2018, bilateral trade in goods and services reached $142.6 billion with a trade deficit of $25.2 billion. In early 2020, India agreed to buy $3 billion worth of military equipment from the US. This deal was followed by an intelligence-sharing agreement into Q4 2020. High tariffs have, however, derailed trade agreements between the two countries.
In 2020, the US trade deficit with India rose 1.7% to $23.8 billion, owing to high equalization levies by Indian authorities on merchandise trade. Exports were $27.4 billion (a decrease of 20.1%), while imports also lowered 11.3% to $51.2 billion. The increase in the deficit was attributed to high tariff and non-tariff barriers. India’s most-favored-nation (MFN) rates are the highest among World Trade Organization states at 17.6% and are highly restrictive.
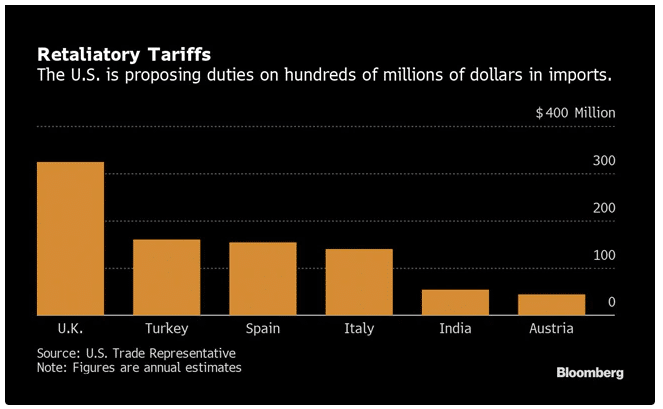
US-retaliatory tariffs
The US classified India among six nations taxing internet-based companies. In retaliation, the US is planning to impose tariffs worth $1 billion on an annual basis. The tariffs could hit a high of 25%, according to the US Trade Representatives. The tariffs placed on India and Austria by the US could reach almost $100 million. India’s digital service tax on US companies will be 2% into 2021. This tax means that the companies will pay up to $55 million annually to operate in India.
Technical analysis
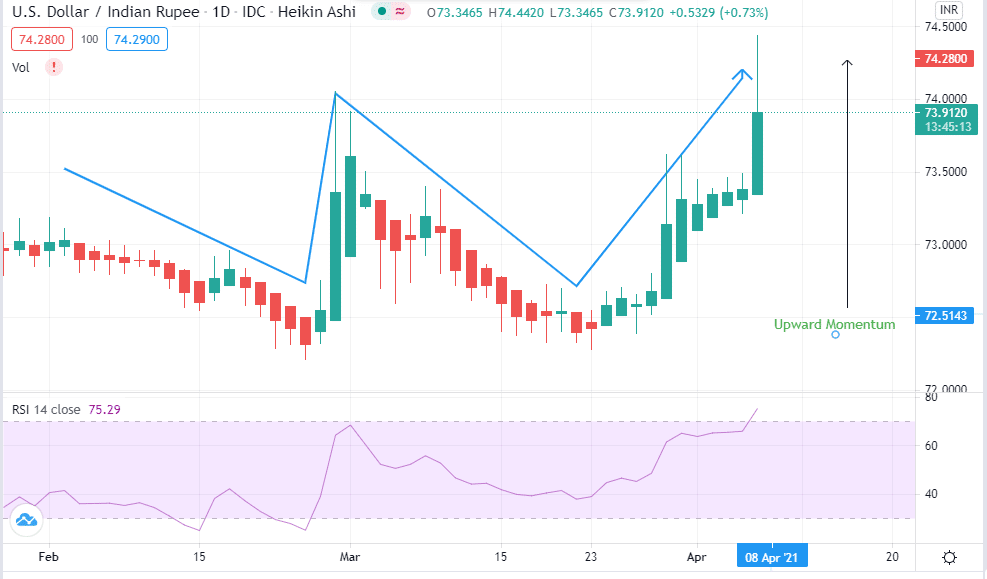
USD/INR
The daily chart shows that USD/INR is headed for upward momentum. The 14-day RSI is at 75.29, indicating that investors are headed into the overbought zone. The path of the price trendline from February 2021 also supports an uptrend in April 2021 to favor a bullish market for the dollar.








Leave a Reply