
Identification of trends is one of the most important aspects of trading. It is not uncommon for a stock to trade sideways for prolonged periods. At times, however, markets may become volatile, thereby making it difficult to identify where the trend is headed. That is why we need oscillators.
RSI
This indicator signals to traders how strong or weak a particular market trend is. This is indicated when the asset becomes overbought (indicated by movement above 70) or oversold (movement to figures below 30), based on a scale that ranges between 0 and 100.
In addition to showing the momentum of sales and buys, the RSI is a key tool in showing the likely points at which resistance levels and support levels will be established. This helps traders to estimate points at which divergences are likely to occur, as well as likely reversals.
For a divergence that is assuming a bullish trend, the RSI will have its reading go up to oversold territory, with new lows and new highs being recorded. This usually sets the stage for a strong market rally. A bearish divergence will be characterized by a slide into overbought territory (RSI above 70). Importantly this is usually followed by higher highs as well as lower highs, both of which signify a break from a trend.
Stochastic Oscillator
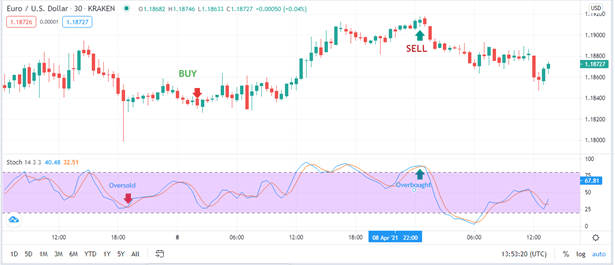
This is an indicator used to spot the highs and lows of price movements within a short time span. It uses two indicator lines, namely %D and %K lines. The %D line is the slower line, while the %K line is faster.
This tool is based on the general belief that during an upswing, closing prices are usually within small margins of previous highs. If, however, the price is rising, but the closing prices begin heading down, then we know that there’s a high chance that the market momentum is weakening. By looking at the behavior of the price trend line in the recent trading sessions, we can estimate reversal points more accurately. The more the price action comes near daily lows, the more likely a bearish reversal is to occur. Using the same logic, the more the price movements stay near the daily highs, the more likely a bullish action will happen.
The %K and %D lines give more reliable information when either of them crosses the other. This is called a crossover. However, even in such an instant, using the stochastic oscillator alone is not the best way to trade. You should employ other relevant indicators too and evaluate market fundamentals as well.
Crossovers
The crossover refers to a situation whereby the %К and %D curves intersect. The intersection between the two curves is a key signal when dealing with the stochastic oscillator. With this tool, we know that the bears are taking charge when the %K curve cuts through the %D curve while headed downwards. On the other hand, we know that the bulls are taking charge when the %K line crosses the %D line from down to up. Using these two points of intersection, you should place your support or resistance levels within 2 or 3 units of the crossovers.
Convergence and divergence between RSI and Stochastic Oscillator
As earlier mentioned, it is not advisable to use a single indicator when making trading calls. To minimize the probability of making erratic calls, it is prudent that you employ both of them. By their functionality, the two indicators serve different purposes.
RSI is a measure of how strong or weak the prevailing momentum is. Stochastic Oscillator shows us how close or how far the prevailing price is to the most recent highs and lows. It follows, therefore, that the RSI is appropriate when the market has developed either a well-defined upswing or downtrend. The Stochastic Oscillator should be employed when the trend has been sideways.
Based on its characteristics, the RSI is, therefore, a good tool for determining whether the prevailing market trend is likely to be broken. In the case of Stochastic Oscillator, it is an ideal tool when a trader wants to assess the chances of a breakout from the current trend. This is achievable by looking at whether or not the current price has broken outside the most recent high-low range.
The two indicators are both useful when we want to know whether an asset has assumed an oversold status or has been overbought. With the RSI, movement past the 70 mark will represent an overbought asset, while anything below 30 will tell the trader that the asset has been oversold. For Stochastic Oscillator, we will know that the asset has been overbought when it is under the 20 mark, and the oversold signal will come when it climbs above 80.
Weaknesses of Relative Strength Index (RSI)
RSI has a significant weakness in that it is often not in tandem with the market trend. When the RSI strengthens, the price trend usually becomes weaker and vice versa. This is to say that a strong bullish or bearish trend will render the RSI less reliable. Conversely, a weak market trend often has a correspondingly strong and more valuable RSI.
It follows, therefore, that it is not possible to identify a looming reversal/breakout in price by only considering whether or not an asset has been overbought or oversold. For example, a stock can spend a significant amount of time in the oversold or overbought territory without resulting in a price reversal. This can happen if, for example, the overbought position results in a situation whereby supply sources are faced with shortages or if buyers are keen to hold on to the asset.
Weaknesses of the stochastic oscillator
Like the RSI, the Stochastic Oscillator, when relied on without supportive evidence can mislead us into making the wrong calls. Volatile markets, for example, are difficult to predict and can send the price action against the signals given by the stochastic oscillator. This, therefore, means that the Stochastic Oscillator should also be backed up by other technical indicators and market fundamentals.
Bottom line
The RSI and Stochastic Oscillator have specific applications in trading. However, they are not self-sufficient for trading and should therefore be used together with other technical indicators and market fundamentals. This will ensure that their strengths are complemented, and the margin of error will be minimized.








Leave a Reply