Cryptocurrencies and currency pairs are some of the most traded instruments in the capital markets. While investors use an array of tools to trade the two, futures have always stood out, given the synergies they offer.
What are futures?
Futures are derivatives that allow investors and traders to buy or sell a commodity at a specific price in the investment world. The settlement is not done at present but at a set price in the future.
Being a contract agreement, it involves two parties, the buyer, and the seller, who do business on exchange markets like the CME group.
How futures work
While trading cryptocurrencies or FX using futures contracts, traders have the opportunity to either buy or sell the underlying asset. For instance, investors are simply looking to profit from significant price appreciation whenever they buy. When the asset price increases, they make money on the difference between the buying price and the final settlement price.
Likewise, it is possible to profit from forex and cryptocurrency prices depreciating. A profit is generated when a trader enters a sell, or short position and the price declines significantly. The profit will be the difference between the price at which the sell position was triggered and the final price.
What are Cryptocurrency futures?
Cryptocurrency futures allow traders to bet on cryptocurrencies’ future prices. Investors gain exposure by selecting the coins without actually buying them. Traders only look to profit from price differentiation. The crypto derivatives trade on the CME exchange as well as in cryptocurrency exchanges.
There must be two players in the trade for the contracts to work: the buyer and the seller. The contracts also come with a specific number of units that one is purchasing as one does not buy the actual asset. Marginal requirements and settlement methods are also specified.
The expiration date: It refers to when the agreement entered must be settled. If one party enters a buy, the other party has to sell at the pre-agreed price and date in the future. In some cases, traders can settle their contracts before the settlement date to other investors.
Units per contract: It refers to the worth of each unit purchased, representing the underlying assets. In the case of the CME market, one bitcoin future is usually valued at 5 bitcoins.
Leverage: most exchanges on which crypto futures are traded allow users to borrow some money that they can use to increase the size of their trades. Leverage varies from one platform to another, with some allowing the purchasing power to increase by up to 50 times.
Crypto futures settling
Cryptocurrency futures contracts can be settled in two ways:
Physical settling: With this type of settling, the buyer receives the actual item being purchased, i.e., Bitcoin.
Cash settled: There is no actual transfer of the asset purchased in this case. Instead, there is a cash transfer between the two parties involved in the agreement.
Bitcoin crypto future trade example
Suppose a trader purchased two BTC futures contracts totaling 10 Bitcoin. If the price of a single BTC futures contract was $5,000, the value of both contracts would be $50,000. If the margin requirement in the exchange in which the futures contract is being traded is 50% of the contract, the investor would have to deposit $25,000 as a margin to trade the two contracts. In return, they can finance the rest using leverage.
Cryptocurrency futures can be traded in various cryptocurrency exchanges, including Binance, the largest by trading volume. CME FTX and OKX are other exchanges that support such types of derivatives for trading cryptocurrencies.
Benefits of trading cryptocurrency futures
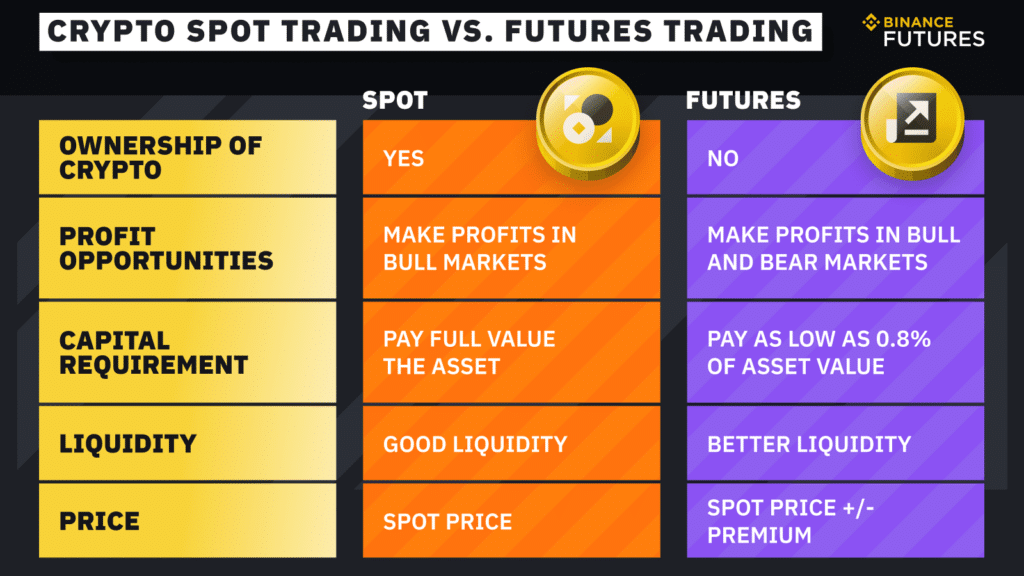
Simple: Futures contracts simplify the process of trading and profiting from cryptocurrencies. Given that one does not take direct ownership of the asset, there is no need for a crypto wallet.
Safer option: Futures contracts are a safe option for trading cryptos as they come with position and price limits that curtail risk exposure. In addition, one averts the risk of losing anything on wallets being hacked.
The risks
Leverage risk: While leverage increases the prospect of generating significant returns, the risk of losses exponentially increasing is usually high while trading cryptocurrencies on a margin.
Trading forex futures
Forex futures contracts are similar to cryptocurrencies futures as they obligate a buyer and seller to transact at an agreed price and predetermined time in the future. The contracts are entered on the underlying asset, which in this case can be EURUSD, GBPUSD, etc. Forex futures are cash-settled upon expiry before the expiry date.
How do they work?
Forex futures are standardized contracts that trade on centralized exchanges. At expiry, the contracts are settled by simply changing the amount indicated in the size of the contract. In the case of cash-settled futures, settling takes place daily, depending on the price changes.
Forex Futures components
Underlying asset: The currency pair being traded indicates the exchange rate.
Expiration date: It indicates the date the contract must be settled. This is the date at which the currencies are exchanged for physical delivery.
Size: Affirms the size of the contracts being traded. The sizes are standardized depending on currencies. For instance, euro currency contracts are standardized at 125,000 euros.
Margin requirement: defines the amount of money that must be in the account to trade the derivatives. If the margin falls below the level, a margin call is triggered, requiring one to deposit or stand to take a loss.
Currency futures uses
Speculators mostly use them to profit from exchange rate changes. If a buyer expects the rate to increase, he could enter a long position by buying FX futures contracts. Should the exchange rate increase, the trader would profit based on the difference between the two prices and the units purchased.
Forex futures are also used for hedging purposes, whereby companies and forex traders lock in an exchange rate. Consequently, they would be able to acquire a given currency at an agreed price in the future, therefore avoiding the negative pitfalls of exchange rate changes.







Leave a Reply