
- US net-interest costs are expected to grow from 1.4% of GDP in 2021 to 2.4% in 2031.
- European banks have not recovered from a €2 trillion debt in more than a decade.
- Increased spending will help the US economy to recover despite the rise in debt.
The EUR/USD trading pair has risen by 2.76% in the three months leading to February 16, 2021, buoyed by the falling unemployment rate in Europe. A further slump of the US dollar is expected later as the forecasts predict a high federal deficit ahead of the stimulus rollout. Uncertainty reigns in President Biden’s planned spending of the coronavirus aid that saw Republicans opt-out of the voting process.
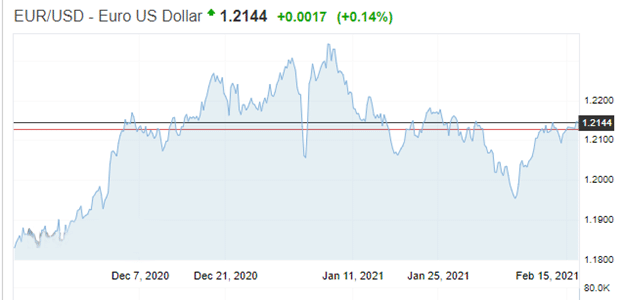
The French unemployment rate declined by 8.0% in Q4 2020 from an upside of 9.1% in the previous quarter.
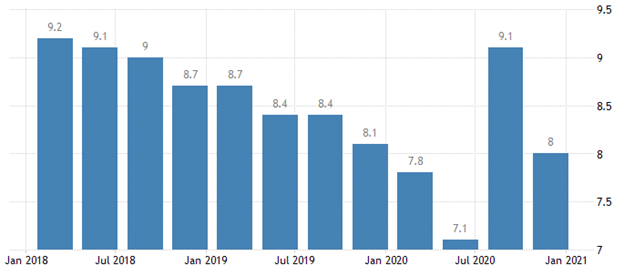
This rate fell to the pre-coronavirus period after six weeks of intense lockdown. The French president was optimistic that the country would attain a 7% reduction in unemployment at a high of 9.5% in 2017. A positive increase in employment levels put a positive mark on the euro against the dollar.
Unemployment in the eurozone in December 2020 remained constant at 8.3%. Although the number of jobless claims in the 19 countries sharing the euro rose by 0.4% MoM (from 13.671 million in December 2020 to 13.616 million in November 2020), this figure persisted.
However, European banks, Germany’s Commerzbank AG among them, have announced that it will slash a third of its staff and reduce branches owing to investor pressure. Thousands of units are scheduled for closure in Italy and Spain due to bank mergers with clear overlapping roles. These banks are seen to have low lending growth as compared to their US counterparts.
The European banks have been unable to fully recover from the 2008 financial crisis with over a €2 trillion loan. This debt alone represents up to 40% of the entire loan book of the banks. Additionally, with the eurozone operating at negative rates, these banks may find it hard to recover their profits.
The US federal budget
The US federal budget deficit is expected to hit $2.3 trillion by the second half of 2021. However, this deficit is an improvement from the FY 2019-2020 that stood at $3.1 trillion.
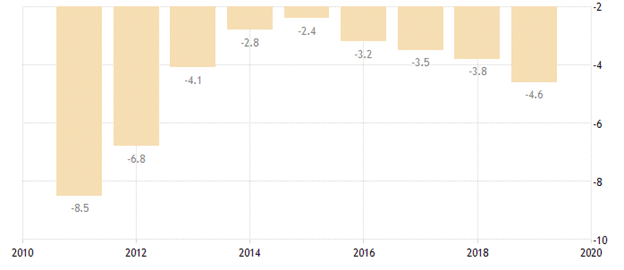
The US Federal budget deficit as of 2019 was 4.6% of the GDP. This rate represented an increase of 0.8% from the previous reading of 3.8% in 2018. The monthly budget deficit in January 2021 hit a high of $163 billion, surpassing market expectations tagged at $150 billion. Passage of the $900 billion coronavirus aid package in 2020 made the first four months of the FY 2021 begin with a record deficit of $736 billion.
We expect that the US’s economic output will tilt towards recovery and reach pre-pandemic heights before 2022. Inflation and interest rates may increase with the decline of Federal Spending even if Congress approves Biden’s relief package. Expenditures will increase in healthcare, aid rescue initiatives, and compensation for unemployment cases.
Data from the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) shows that increased spending has boosted the US economy from 2020. However, the net-interest costs will grow to almost $800 billion (representing 2.4% of the US GDP in FY 2031). As of FY 2021, net-interest prices were at $303 billion (or 1.4% of the GDP).
Technical analysis
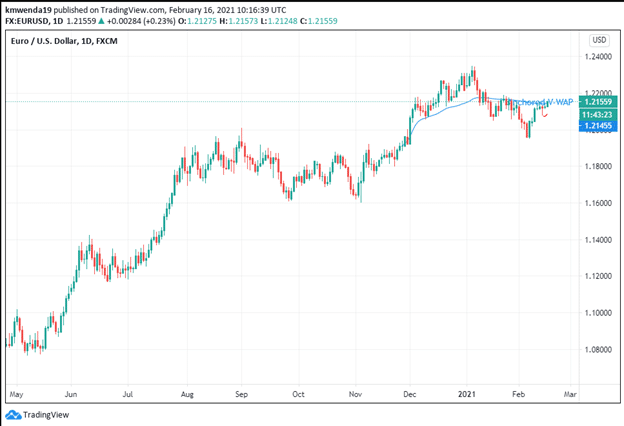
The anchored V-Wap shows that the EUR/USD trading pair may move towards the weighted average price above 1.2200. Positive short-term sentiment may continue pushing the euro above the dollar. Increasing debt risk may put a small lid on the dollar’s breakout. However, the passage of the stimulus later in February 2021 may give the dollar a springboard for a breakout.








Leave a Reply