
The crypto market is renowned for its wild and frequent price swings. At face value, this makes it one of the riskiest asset classes. However, for the risk-tolerant investor, this can be interpreted as having numerous opportunities for profit if one could capitalize on these price fluctuations. To that end, one of the most popular techniques such investors employ is scalping. The good news is that scalping has been in use for decades in several other traditional markets, where it has yielded impressive results. Let’s look at what this tried and tested strategy entails for crypto enthusiasts.
Crypto scalping explained
This is a short-term trading strategy that aims at profiting from the frequent price movements that dot crypto price charts. Usually, it aims at the small movements, as these tend to be the most frequent. The idea is that by accumulating small profits from each of these trades, the scalper could take home a sizeable profit at day’s end.
The crypto market is well suited for this trading style, owing largely to its high volatility. However, scalpers often have to react quickly, entering and exiting trades in the space of a few minutes. To succeed as a scalper, you need to be quick on your feet and consistent with your opportunity capitalization.
To increase their profit margins, some scalpers will utilize leverage. This allows them to amplify their profits, but on the flip side, it also amplifies any losses they suffer. One should be careful not to overleverage, as one large loss is enough to offset profits accumulated from several successful trades.
How scalping works
As aforementioned, scalping is, by design, a short-term trading strategy. The best timeframe for it is anywhere between the 5 to the 30-minute chart. This is because the shorter the timeframe, the more potential trade setups there are for you to profit from. Some scalpers utilize even shorter timeframes, some even lower than 1 minute. However, humans are not very good at analyzing plenty of information in such short timeframes; instead, bots tend to outperform most humans.
Since we mentioned bots, let’s segue into the two major approaches to scalping. These are manual and automated scalping. The latter, as you can imagine, involves the use of algorithmic bots that follow a predetermined strategy to place and close trades. Such programs are capable of autonomously performing trades even when the trader is not actively monitoring the markets.
The second approach is manual trading. This involves personally monitoring the charts and placing trades whenever the chance presents itself. Under manual scalping, some traders tend to rely on their gut feeling to place trades rather than a set-in-stone strategy. These are called intuitive scalpers. Other traders are more technical, and they religiously follow their stipulated strategies to qualify potential trade setups. Such is referred to as systematic scalpers.
Best scalping strategies
Range trading
Oftentimes, when the market is not trending, prices may be stuck within a range. During such periods, prices tend to bounce between a support and resistance level, which is very discouraging for trend traders. However, for scalpers, this presents a unique opportunity to buy at support and sell at resistance.
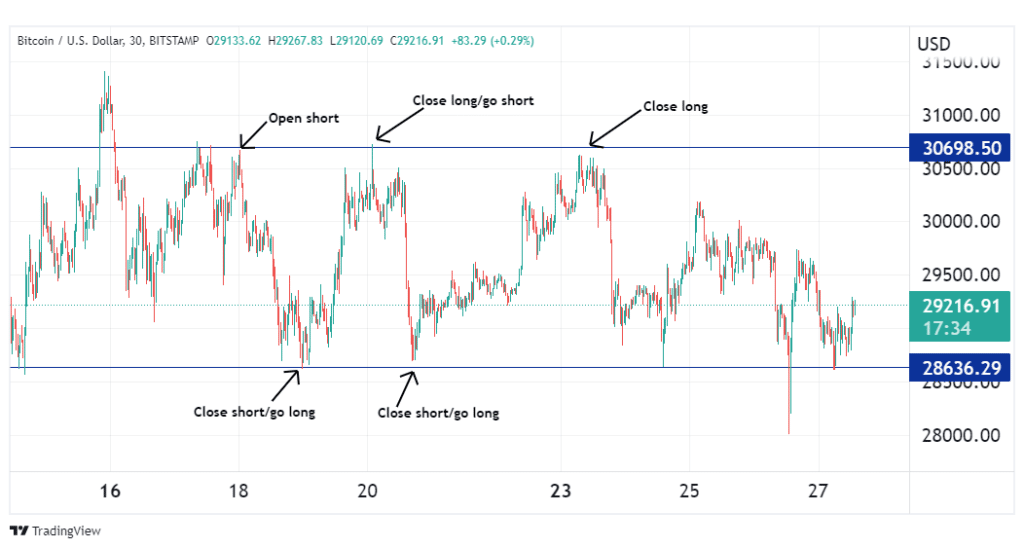
A stop-loss is paramount when trading these ranges so as to prevent losses from sudden breakouts.
Arbitrage trading
Sometimes, similar assets may be priced differently on different platforms. For instance, ETH may be priced higher on Kraken than on Coinbase. On noting this, a scalper could buy several units of ETH on Coinbase and immediately sell them on Kraken at a profit. This type of trade is called arbitrage trading. Again, since humans are not very good at noticing such price discrepancies, this avenue is saturated with bots. Arbitrage trading helps equalize prices of crypto assets across exchanges.
Margin trading
Since scalping aims at small profit amounts per trade, sometimes these profits may seem negligible, especially if you don’t have a large account balance to begin with. To remedy this, scalpers take out the leverage offered on most exchanges, which allows them to trade with higher amounts than they currently hold. This has the effect of multiplying their profits. However, if they make a loss instead, that would be multiplied as well.
Trading the bid-ask spread
The bid-ask spread is the difference between a crypto asset’s bid and ask price. When the asking price is unusually high while the bid price is unusually low, this means that there are more traders buying the asset than those that are selling it. The increased demand drives up the asset’s price, which prompts scalpers to sell their holdings.
Conversely, when the asking price goes unusually low while the bid price rises, it creates a narrow spread as the sellers saturate the market. In such instances, the scalpers will be looking to buy the asset while its price is low.
Pros of scalping
- Due to the straightforward nature of scalping as a strategy, it lends itself well to automation. There are several scalping bots one can employ, which can help prevent emotional trading. On platforms such as Bitsgap, one can even create their own scalper bot from scratch without coding.
- Since scalping aims at close profit targets, scalpers tend to use tight stop-losses, which minimize their risk.
- Due to the high volatility characteristic of crypto markets, scalpers are guaranteed several trade opportunities in a day, which translates to more profits.
Cons of scalping
- Each scalp trade is charged transaction fees, which can get expensive in the long run.
- The use of leverage can easily blow one’s account if the market goes against you.
- The market is saturated with bots, which provide unfair competition to manual scalpers.
Summary
Scalping is a popular short-term trading strategy that accumulates profits from several trades within a day. Due to its straightforward nature, it is easily automated. Scalpers could also utilize leverage to amplify their profits. However, appropriate risk management measures should be taken so as to avoid large losses.








Leave a Reply